The therapeutic effect of medium frequency electrotherapy
Release time:2024-09-19 15:13
Source:
Page view:724
Medium frequency electrotherapy is one of the most familiar physical therapies for rehabilitation treatment. It is often used for common diseases such as cervical spondylosis, lumbar disc herniation, muscle strain, ligament sprain, and frozen shoulder. However, many people often misunderstand medium frequency. In fact, the medium frequency electrotherapy instruments we commonly use include a variety of medium frequency electrotherapy and low frequency electrotherapy, which can modulate electrotherapy programs with multiple frequencies and waveforms.
What is the real medium frequency electrotherapy?
Medium frequency electrotherapy
Definition: The method of treating diseases with pulse currents of 1 to 100kHz is called medium frequency electrotherapy.
The current frequency used in medium frequency electrotherapy is mostly between 2000 and 8000Hz. According to the different generation methods, waveforms and frequencies of the medium frequency current used, medium frequency electrotherapy can be divided into:
Interference electrotherapy: ① Traditional interference electrotherapy; ② Dynamic interference electrotherapy; ③ Stereo dynamic interference electrotherapy.
Equal amplitude medium frequency electrotherapy: ① Audio electrotherapy; ② Audio electromagnetic field therapy; ③ Ultrasonic frequency electrotherapy.
Modulated medium frequency electrotherapy: ① Sine modulated medium frequency electrotherapy; ② Pulse modulated medium frequency electrotherapy. Low and medium frequency electrotherapy: ① Music electrotherapy; ② Wave electrotherapy.
The circuit formed by the current acting on the human body
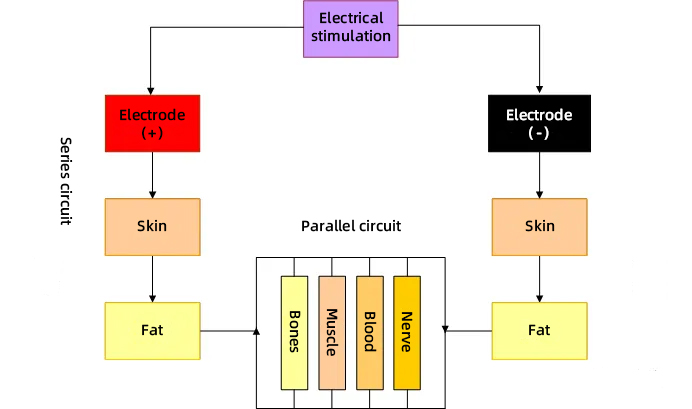
The circuit in which electric current acts on the human body
The conductivity of different tissues:
Blood: contains a lot of water and ions, and is the best conductor.
Muscle: 75% water, but depends on the movement of ions when the muscle contracts, when the ions move longitudinally, it can conduct more electricity. Tendons are denser than muscles and have less water, so they are considered poor conductors.
Fat: Only 14% water, considered a poor conductor.
Peripheral nerves: The conductivity is 6 times that of muscles, but the nerves are wrapped in fat and nerve sheaths, which are poor conductors.
Bone: Extremely dense, only 5% water, the worst biological conductor.
Compared with low frequency, medium frequency produces less skin resistance, so it can act with greater intensity without causing the discomfort of low frequency of the same intensity.
Therapeutic effect
Promote local blood circulation:
Instantaneous hyperemia reaction: The local hyperemia reaction is not obvious when the medium frequency electricity is applied once or when it stops. The local hyperemia reaction is more obvious 10 to 15 minutes after the action stops. This can be explained by axon reflex and triad reaction (axon reflex means that when the current acts on the human body surface, the electrical stimulation is transmitted through the afferent nerve to the posterior horn of the spinal cord, the efferent nerve is excited, and the small arteries of the skin are dilated, resulting in diffuse redness on the skin surface under the electrode. When the skin is stimulated, histamine, substance P, acetylcholine, etc. are also released, which can dilate the arteries. In addition, electrical stimulation itself can directly cause arterial dilation). The improvement of blood circulation in muscle tissue is related to the chemical substances produced by muscle activity (the metabolites of muscle activity, such as lactic acid, ATP, ADP, etc., have obvious vasodilation effects). The improvement of blood circulation in deep tissue or distant tissue is related to the influence of autonomic nerves.
The improvement of blood circulation after multiple treatments: It is the result of the cumulative effect of single action and the adjustment of autonomic nerve function.
Analgesic effect
Medium frequency electricity has a relatively good analgesic effect, and its mechanism has two forms:
Instant analgesic effect: different degrees of analgesia can be observed during single treatment and after the cessation of several medium frequency electricity treatments, and this immediate analgesic effect can last for several minutes to several hours.
There are many explanations for the immediate analgesic mechanism: the neural mechanism is explained by the gate control theory and the layer interference theory, and the humoral mechanism is explained by 5-hydroxytryptamine, endogenous morphine-like substances, etc.
Analgesic effect after multiple treatments: The analgesic effect after multiple treatments can be explained by the combined effect of various factors that produce immediate analgesic effects and the combined effect of various effects that cause local blood circulation to be enhanced through axon reflexes.
Anti-inflammatory effect
Medium frequency electricity has a good therapeutic effect on some chronic nonspecific inflammations, mainly because the blood circulation of local tissues is improved after the medium frequency electricity action, tissue edema is reduced, the absorption and excretion of inflammatory products are accelerated, the nutrition and metabolism of local tissues are enhanced, and the immune defense function is improved.
Softening scars and loosening adhesions
Medium frequency electricity has a good effect of softening scars and loosening adhesions. This is because medium frequency electrical stimulation can expand the gap between cells and tissues, so that the adherent connective tissue fibers, muscle fibers, nerve fibers, etc. can be separated after activity.
Effect on skeletal muscle
Medium frequency current stimulates motor nerves and muscles to cause normal skeletal muscle and denervated muscle contraction, which has the effects of exercising skeletal muscle, preventing muscle atrophy, increasing smooth muscle tension, and adjusting autonomic nerve function.
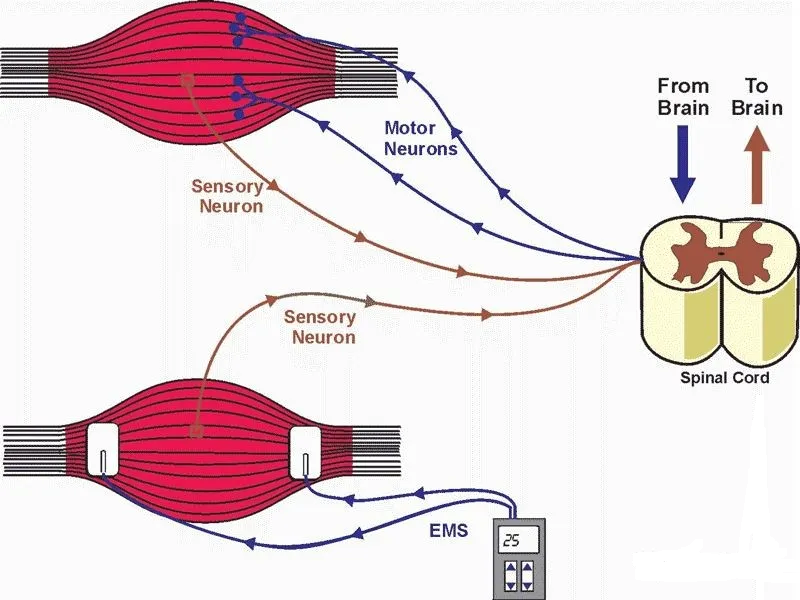
The effect of electrical stimulation on skeletal muscles
Effect on biomembrane permeability
Under the action of sinusoidal medium frequency current, the number of drug ions and molecules passing through the active biomembrane is significantly greater than the number of inactive biomembranes. It is believed that medium frequency current can increase the permeability of active biomembranes, and its mechanism may be to increase the intercellular gap.
